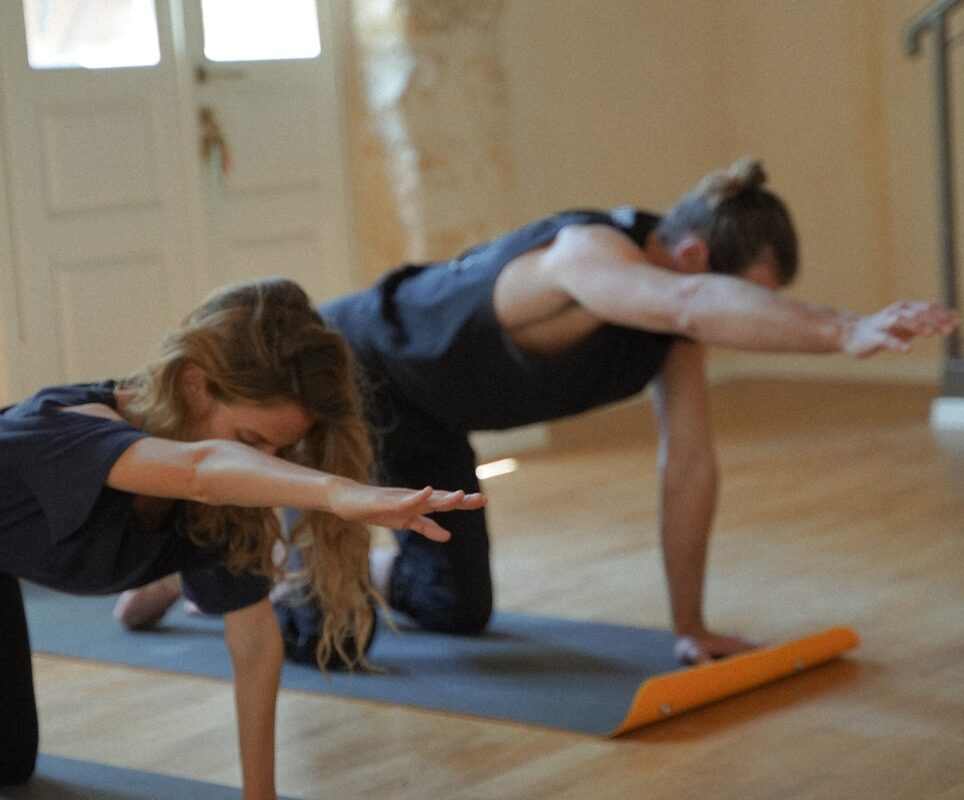
Mobility is a term that is often used in the context of physical fitness and wellness. It refers to the ability of a person’s joints to move through a full and unrestricted range of motion. This is an important aspect of overall physical health, as it allows individuals to perform a wide range of movements and activities with ease and without discomfort or pain.
There are many benefits to having good mobility. For athletes, it can help to improve performance and reduce the risk of injury. This is because having good mobility allows athletes to move more freely and efficiently, which can help them to achieve better results in their chosen sport. In addition, having good mobility can help to reduce the risk of overuse injuries, which are common among athletes who do a lot of repetitive movements.
For regular people, having good mobility can also be beneficial. It can help to improve overall physical health and fitness, as well as help to reduce the risk of chronic conditions such as obesity, heart disease, and diabetes. In addition, having good mobility can help to improve quality of life and independence, as it allows individuals to perform everyday tasks and activities with ease and without discomfort or pain.
So what is the difference between mobility, movement, and flexibility? These terms are often used interchangeably, but they do have slightly different meanings. Movement refers to the ability of the body to move from one position to another. This can include anything from walking and running to more complex movements such as dancing or playing sports. Flexibility, on the other hand, refers to the ability of the body to move its joints and muscles through a full range of motion. This is an important aspect of mobility, as it allows individuals to move freely and without discomfort or pain.
Overall, mobility is an important aspect of physical fitness and wellness. It allows individuals to move freely and perform a wide range of movements and activities with ease. For athletes, having good mobility can help to improve performance and reduce the risk of injury. For regular people, having good mobility can help to improve overall health and fitness, as well as quality of life. It is important for individuals to incorporate mobility training into their fitness routine in order to maintain good mobility and overall physical health.
Common Mobility Exercises
Foam rolling
This is a self-myofascial release technique that involves rolling various parts of the body over a foam roller to help release tension and improve mobility.
Dynamic stretching
This type of stretching involves moving the body through a full range of motion in order to warm up the muscles and improve mobility.
Static stretching
This type of stretching involves holding a stretch for a period of time in order to lengthen the muscles and improve flexibility.
Lunges
This exercise involves stepping forward with one leg and lowering the body down until the back knee is close to the ground. This helps to improve mobility in the hips and legs.
Squats
This exercise involves lowering the body down as if sitting back into a chair and then standing back up. This helps to improve mobility in the hips and legs.
Push-ups
This exercise involves lowering and raising the body using the arms and hands, which helps to improve mobility in the shoulders and arms.
Planks
This exercise involves holding the body in a straight line supported by the hands and toes, which helps to improve mobility in the core muscles.
Bird dogs
This exercise involves extending opposite arms and legs while maintaining a straight back, which helps to improve mobility in the core and limbs.

What Causes Bad Mobility?
Bad mobility, or reduced range of motion in the joints, can be caused by a variety of factors. Some of the most common causes of bad mobility include:
Inactivity: When the body is not used regularly, the muscles and joints can become stiff and weak. This can lead to reduced mobility and an increased risk of injury.
Age
As people age, their muscles and joints naturally become less flexible and more prone to stiffness. This can lead to reduced mobility and increased risk of falls and other injuries.
Overuse injuries
Repetitive or intense physical activities can put a lot of strain on the muscles and joints. This can lead to overuse injuries, such as tendinitis or bursitis, which can cause reduced mobility.
Poor posture
Poor posture can put unnecessary strain on the muscles and joints, leading to stiffness and reduced mobility.
Obesity
Excess body weight can put additional strain on the muscles and joints, leading to stiffness and reduced mobility.
Chronic conditions
Certain chronic conditions, such as arthritis or fibromyalgia, can cause inflammation and stiffness in the muscles and joints, leading to reduced mobility.
Trauma
Traumatic injuries, such as sprains or fractures, can cause damage to the muscles and joints, leading to reduced mobility.
There are several ways to improve mobility and prevent bad mobility from occurring. Some evidence-based strategies include:
Regular physical activity
Engaging in regular physical activity can help to improve flexibility and strength, leading to better mobility. This can include activities such as walking, swimming, or stretching.
Proper posture
Maintaining good posture can help to reduce strain on the muscles and joints, leading to improved mobility. This can include standing and sitting up straight, avoiding prolonged periods of sitting or standing, and using ergonomic equipment.
Weight management
Maintaining a healthy body weight can help to reduce strain on the muscles and joints, leading to improved mobility. This can be achieved through a combination of regular physical activity and a balanced diet.
Strength training
Engaging in regular strength training can help to improve muscle strength and joint stability, leading to improved mobility. This can include exercises such as squats, lunges, and push-ups.
Stretching
Regular stretching can help to improve flexibility and range of motion in the muscles and joints, leading to improved mobility. This can include dynamic stretches before physical activity, and static stretches after physical activity.
In conclusion, bad mobility can be caused by a variety of factors, including inactivity, age, overuse injuries, poor posture, obesity, chronic conditions, and trauma. By incorporating regular physical activity, proper posture, weight management, strength training, and stretching, individuals can improve their mobility and prevent bad mobility from occurring.